数据结构实验四:队列
数据结构实验四:队列
队列的基本操作
1 实验目的
- 掌握队列的顺序及链式存储结构
- 验证顺序队、链队及其他们的基本操作实现
- 验证队列的操作特性
2 实验内容
- 建立一个空队
- 对已经建立的队列进行进队、出队等基本操作。
3 软件程序
3.1 顺序队
sqqueue.cpp:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#define MaxSize 1000
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct Quene{ //定义顺序队
int front; //队头指针
char data[MaxSize]; //存放队中元素
int rear; //队尾指针
}SqQueue; //struct Queue 的别名
void InitQueue(SqQueue * &q)//初始化队列
{
q=(SqQueue *)malloc(sizeof(SqQueue)); //分配一个空间
q->front=q->rear=-1; //置 -1
}
void DestroyQueue(SqQueue * &q)//销毁队列
{
free(q); //释放内存
}
bool QueueEmpty(SqQueue * &q)//判断队列是否为空
{
if(q->front==q->rear){ //首指针和尾指针相等,说明为空
return true; //返回真
}
else{
return false; //返回假
}
}
bool enQueue(SqQueue * &q,char c)//进队
{
if(q->rear==MaxSize-1){ //判断队列是否满了
return false; //返回假
}
q->rear++; //头指针加 1
q->data[q->rear]=c; //传值
return true; //返回真
}
bool deQueue(SqQueue * &q,char &ch)//出队
{
if(q->front==q->rear){ //判断是否空了
return false; //返回假
}
q->front++; //尾指针加 1
ch=q->data[q->front]; //取值
return true; //返回真
}
main.cpp:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include "sqqueue.cpp"
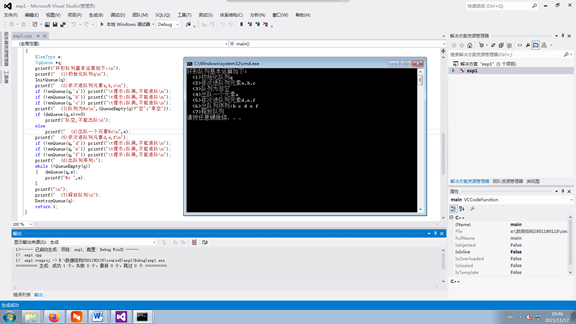
int main()
{
ElemType e;
SqQueue *q;
printf("环形队列基本运算如下:\n");
printf(" (1)初始化队列q\n");
InitQueue(q);
printf(" (2)依次进队列元素a,b,c\n");
if (!enQueue(q,'a')) printf("\t提示:队满,不能进队\n");
if (!enQueue(q,'b')) printf("\t提示:队满,不能进队\n");
if (!enQueue(q,'c')) printf("\t提示:队满,不能进队\n");
printf(" (3)队列为%s\n",(QueueEmpty(q)?"空":"非空"));
if (deQueue(q,e)==0)
printf("队空,不能出队\n");
else
printf(" (4)出队一个元素%c\n",e);
printf(" (5)依次进队列元素d,e,f\n");
if (!enQueue(q,'d')) printf("\t提示:队满,不能进队\n");
if (!enQueue(q,'e')) printf("\t提示:队满,不能进队\n");
if (!enQueue(q,'f')) printf("\t提示:队满,不能进队\n");
printf(" (6)出队列序列:");
while (!QueueEmpty(q))
{ deQueue(q,e);
printf("%c ",e);
}
printf("\n");
printf(" (7)释放队列\n");
DestroyQueue(q);
return 1;
}
3.2 链队
liqueue.cpp:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct qnode
{
ElemType data;
struct qnode *next;
}DataNode;
typedef struct
{
DataNode *front;
DataNode *rear;
}LinkQuNode;
void InitQueue(LinkQuNode *&q)//初始化队列
{
q=(LinkQuNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkQuNode));
q->front=q->rear=NULL;
}
void DestroyQueue(LinkQuNode *&q)//销毁队列
{
DataNode *p=q->front,*r;
if(p!=NULL)
{
r=p->next;
while(r!=NULL)
{
free(p);
p=r;
r=p->next;
}
}
else
free(p);
free(q);
}
bool QueueEmpty(LinkQuNode *q)//判断队列是否为空
{
return(q->rear==NULL);
}
void enQueue(LinkQuNode *&q,ElemType e)//元素进队
{
DataNode *p;
p=(DataNode *)malloc(sizeof(DataNode));
p->data=e;
p->next=NULL;
if(q->front==NULL)
q->front=q->rear=p;
else
q->rear->next=p;
q->rear=p;
}
int deQueue(LinkQuNode *&q,ElemType &e)//元素出队
{
DataNode *t;
if(q->rear==NULL)
return 0;
t=q->front;
if(q->rear==q->front)
q->front=q->rear=NULL;
else
q->front=q->front->next;
e=t->data;
free(t);
return 1;
}
main.cpp:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include "liqueue.cpp"
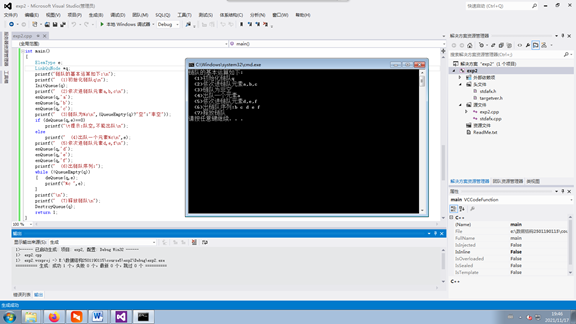
int main()
{
ElemType e;
LinkQuNode *q;
printf("链队的基本运算如下:\n");
printf(" (1)初始化链队q\n");
InitQueue(q);
printf(" (2)依次进链队元素a,b,c\n");
enQueue(q,'a');
enQueue(q,'b');
enQueue(q,'c');
printf(" (3)链队为%s\n",(QueueEmpty(q)?"空":"非空"));
if (deQueue(q,e)==0)
printf("\t提示:队空,不能出队\n");
else
printf(" (4)出队一个元素%c\n",e);
printf(" (5)依次进链队元素d,e,f\n");
enQueue(q,'d');
enQueue(q,'e');
enQueue(q,'f');
printf(" (6)出链队序列:");
while (!QueueEmpty(q))
{ deQueue(q,e);
printf("%c ",e);
}
printf("\n");
printf(" (7)释放链队\n");
DestroyQueue(q);
return 1;
}
4 实验结果
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权